Introduction to TPU Filament
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is a popular 3D printing filament known for its flexibility, durability, and versatility. Unlike standard PLA or ABS filaments, TPU can stretch, bend, and withstand significant wear, making it ideal for projects that require elasticity, resilience, and impact resistance. TPU filament has quickly gained popularity among hobbyists, designers, and engineers alike, providing exciting opportunities in the realm of flexible 3D printing.
What Exactly Is TPU Filament?
TPU, short for Thermoplastic Polyurethane, is a flexible, rubber-like plastic material. It belongs to a class of thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs), which combine the desirable properties of both plastics and rubbers. TPU maintains elasticity and flexibility, yet also offers durability, abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and excellent layer adhesion.
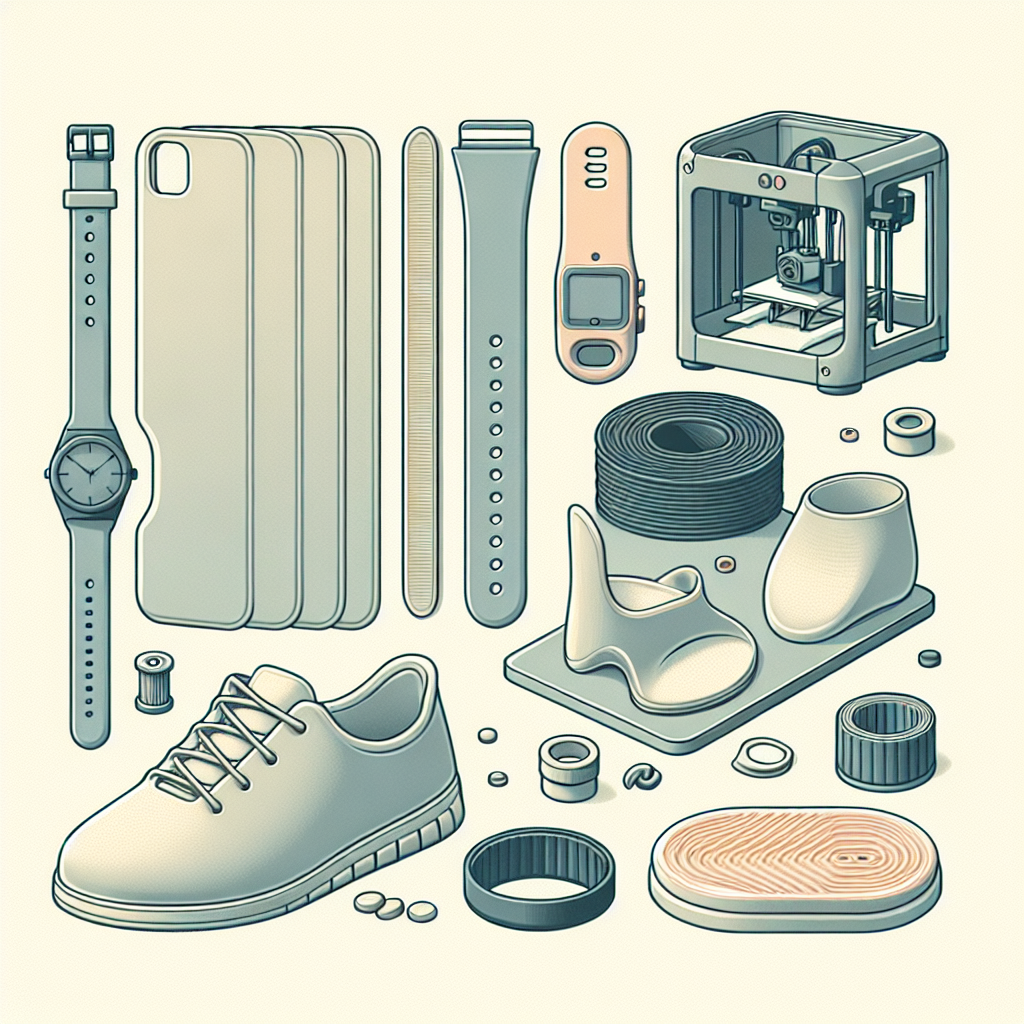
This combination of characteristics allows TPU filament to be used extensively in applications where flexibility and durability are paramount, such as footwear, smartphone cases, wearable devices, seals, gaskets, and shock absorbers.
Key Properties of TPU Filament
- Flexibility and Elasticity: TPU provides outstanding flexibility, allowing it to bend and stretch without losing shape or integrity.
- Durability and Abrasion Resistance: TPU is resistant to damage from constant use, friction, and environmental wear.
- Chemical Resistance: TPU resists oils, greases, solvents, and other chemicals, making it suitable for industrial and functional applications.
- Great Layer Adhesion: TPU prints with excellent layer-to-layer adhesion, resulting in stronger and more durable 3D printed parts.
- Impact Absorption: Its rubber-like quality allows TPU to absorb and dissipate energy from impacts, ideal for protective components.
Benefits of Using TPU for 3D Printing
Versatile Applications
TPU’s versatile nature lends itself to a wide variety of applications—from consumer products like smartphone cases and watch bands to industrial parts such as seals, gaskets, and vibration dampeners.
Superior Durability
Parts printed with TPU can handle stress, strain, and deformation better than traditional plastics, significantly extending the longevity of the printed components.
Enhanced Comfort and Ergonomics
The softness and elasticity of TPU filament make it perfect for wearable items, ergonomic handles, and customized prosthetics, providing a comfortable, skin-friendly feel.
Challenges of Printing with TPU Filament
While TPU offers many advantages, it also presents certain challenges during the printing process, primarily because of its flexibility.
- Retraction Issues: TPU’s elasticity makes retraction settings particularly tricky. Incorrect retraction may lead to stringing or nozzle clogging.
- Slow Print Speeds: Due to its flexible nature, TPU generally requires slower printing speeds to achieve quality results. Speeding up can cause jams or poor layer adhesion.
- Printing Temperature: Finding the optimal printing temperature can require experimentation. Usually, TPU filament prints best at around 210–240°C, but this varies depending on filament brand and printer model.
- Bed Adhesion: Flexible filaments like TPU greatly benefit from heated beds and adhesive solutions such as PEI sheets, blue painter’s tape, or glue sticks to ensure proper adhesion throughout the printing process.
Tips for Successfully Printing With TPU Filament
- Use a Direct Drive Extruder: Direct drive systems reduce the distance between the extruder gear and the hot end, minimizing issues related to filament buckling or jamming.
- Adjust Retraction Settings: Using minimal retraction distances and speeds helps mitigate problems related to flexibility and elasticity.
- Slow Down Your Prints: Keep print speeds around 20–40mm/s for best results. Lower speeds increase quality by improving layer adhesion and reducing vibration.
- Optimize Temperature Settings: Experiment with different temperature settings within the filament manufacturer’s recommended range to find optimal results.
- Ensure Proper Bed Adhesion: Utilize a heated print bed (40–60°C) combined with adhesives to ensure stable first-layer adhesion.
Choosing the Right TPU Filament
When selecting TPU filament, consider a filament’s shore hardness—a scale used to measure flexibility. TPU filaments are typically available in the shore hardness range of 85A (more flexible and softer) to 95A (stiffer yet still flexible). Depending on your specific project requirements, you may opt for softer filaments (for wearable products) or slightly stiffer variations (for industrial or mechanical parts).
Conclusion
TPU filament is an outstanding choice for 3D printing projects requiring flexibility, durability, and resilience. While it comes with unique challenges, proper printer setup, careful adjustments, and patience during the printing process can yield excellent results. By embracing TPU filament in your 3D printing repertoire, you open doors to innovative creations and functional products that other materials simply can’t match.
Leave a Reply