Introduction to 3D Printed Molds for Casting
In recent years, the intersection of 3D printing and traditional casting methods has opened up remarkable opportunities for makers, artists, and industrial professionals alike. Creating molds through additive manufacturing provides precision, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, enabling the production of complex and detailed components. In this guide, we’ll explore how you can confidently create 3D printed molds for casting your own custom parts.
Benefits of 3D Printed Molds
Utilizing 3D printing technology for mold-making offers numerous advantages compared to traditional mold-making methods:
- Rapid Prototyping: Quickly iterate and refine designs without significant time or financial investment.
- Complexity and Detail: Capture remarkable detail and complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional mold-making techniques.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower initial investment and reduced waste since molds can be printed on demand.
- Customization: Easily customize each mold, ideal for short-run or personalized production.
Selecting the Right 3D Printing Technology
Choosing the appropriate 3D printing method is crucial to producing durable, precise molds. Here are the most common technologies suitable for mold-making:
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): Affordable and widely available, FDM printers use thermoplastic filaments. They are excellent for large, sturdy molds, but surface finish quality may require additional post-processing.
- SLA (Stereolithography) & Resin Printing: These printers produce high-resolution models with very smooth surfaces, perfect for intricate details and fine textures. Ideal for jewelry molds or detailed art castings.
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): Ideal for industrial-grade molds that must withstand high pressures or temperatures. Nylon-based powder materials provide durable molds with excellent strength.
Choosing Suitable Materials for 3D Printed Molds
For successful mold printing, it’s critical to select the right material to withstand the casting process:
- PLA: An affordable and easy-to-print option suitable for molds intended for low-temperature casting such as silicone or wax. PLA is less resistant to heat, so not recommended for casting materials with high curing temperatures.
- PETG and ABS: These thermoplastics handle higher temperatures and provide improved durability compared to PLA. They are suitable for moderate-temperature casting applications.
- High-Temperature Resins: Specialized resins designed for SLA printers can withstand extremely high temperatures and pressure, making them ideal for metal casting or injection molding applications.
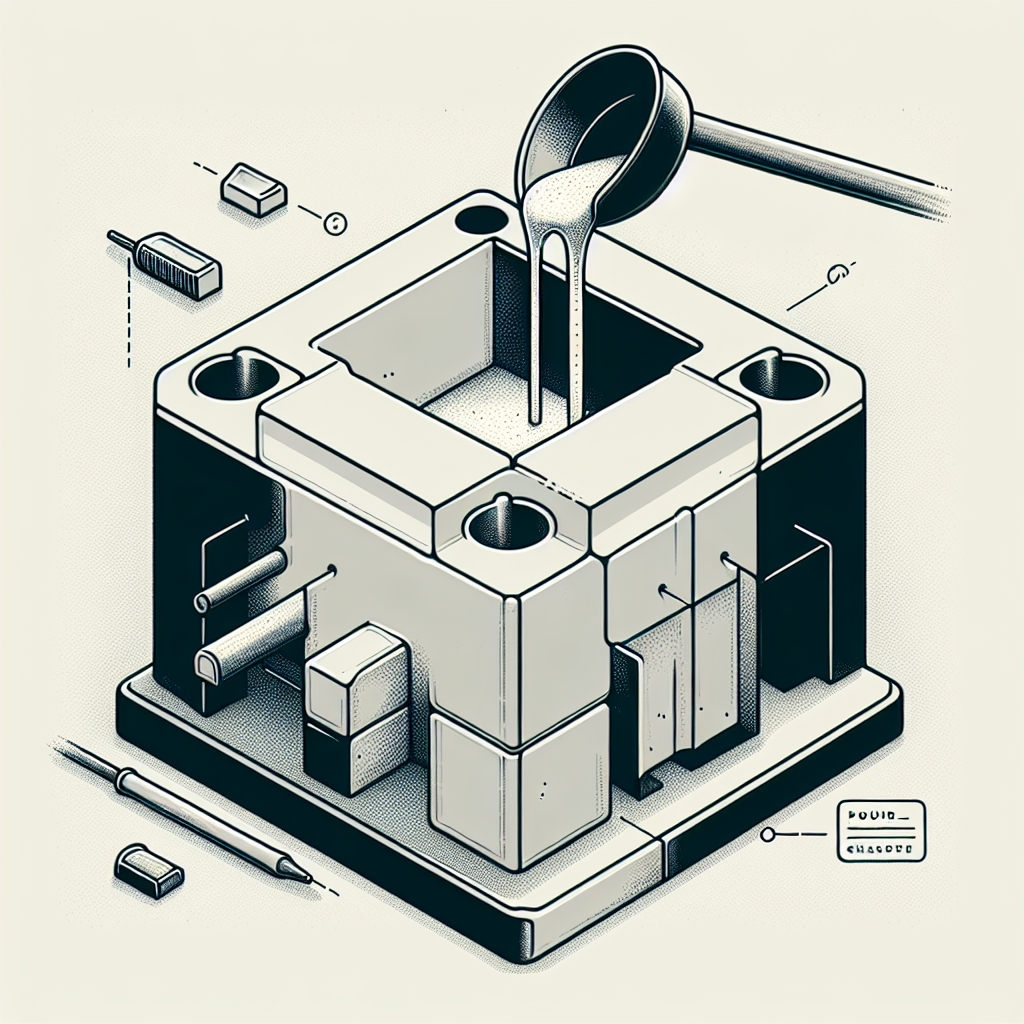
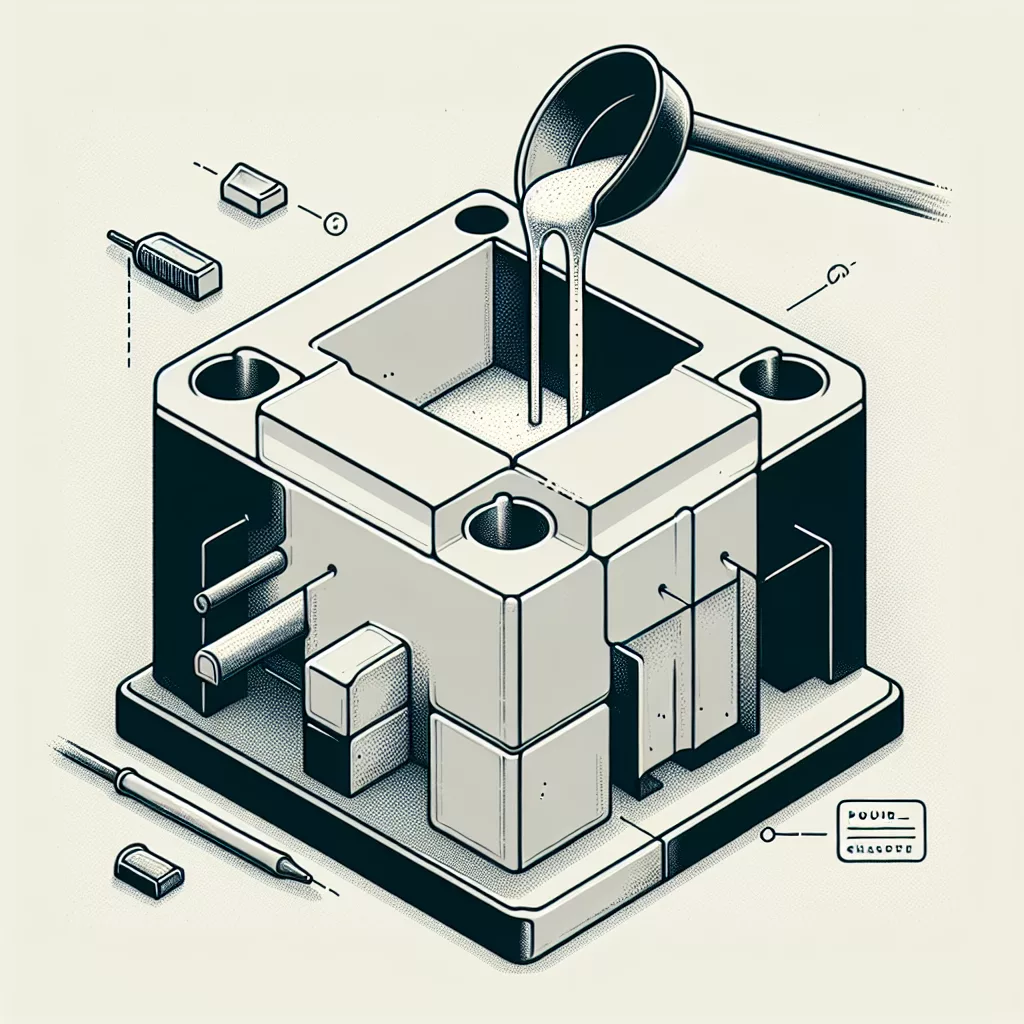
Designing Your Mold for 3D Printing
Proper mold design ensures ease of use during casting and improves the mold’s durability. Follow these guidelines when designing your 3D printed mold:
- Draft Angles: Incorporate slight draft angles (typically between 2° and 5°) on walls to simplify the removal of cast items.
- Venting and Gates: Plan your mold with enough gates, runners, and vent holes, allowing air and gases to escape and ensuring complete, defect-free casts.
- Wall Thickness: Avoid overly thin or thick walls to prevent deformation or cracking during use. Walls between 2-5mm thickness generally give optimal strength and rigidity.
- Alignment Features: Include alignment pins or keys to ensure accurate assembly and repeatable results during casting.
3D Printing and Post-processing Your Mold
Once your design is complete, it’s time to 3D print your mold. Follow these steps for optimal results:
- Optimize Print Settings: Select appropriate print settings such as layer height (lower for higher resolution), infill density (50-100% recommended for mold strength), and support structures if necessary.
- Sanding and Cleaning: After printing, sand or polish mold surfaces as needed to remove layer lines or rough areas. A smooth surface will result in higher-quality castings.
- Surface Sealing: Apply a suitable sealant or mold release agent to ensure easy casting and extend the mold’s lifespan.
Choosing the Right Casting Material
3D printed molds are versatile and can be used with various casting materials. Some common materials include:
- Silicone and Rubber: Popular for prototypes, flexible parts, and medical applications. These materials are easy on molds and require minimal additional preparation.
- Resin Casting: Epoxy or polyurethane resins deliver detailed, high-quality results ideal for decorative objects, figures, and prototypes.
- Wax Casting: Ideal for jewelry making and metal casting applications, wax is easy to cast and remove from molds.
- Metals: For metal casting, high-temperature resins or industrial-grade molds are necessary. Proper preparation and safety precautions are required due to high temperatures.
Ensuring Mold Longevity and Quality Castings
To maximize the lifespan of your 3D printed molds and maintain consistent casting quality, consider the following tips:
- Regular Mold Maintenance: Clean molds thoroughly after each use and inspect them for any signs of wear, cracks, or deformation.
- Proper Storage: Store molds indoors, away from prolonged sun exposure, humidity, or extreme temperatures.
- Release Agent Application: Consistently apply mold release agents to reduce wear and ensure castings remove cleanly and effortlessly.
Conclusion
Creating 3D printed molds for casting opens boundless possibilities in prototyping, manufacturing, art creation, and beyond. By understanding suitable printing technologies, materials, and effective mold design strategies, you can leverage the potential of 3D printing to produce accurate, repeatable, and high-quality castings. Embrace this exciting fusion of traditional manufacturing and modern technology to elevate your crafting and production capabilities to new heights.

Leave a Reply