Introduction: The Intersection of 3D Printing and Medicine
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as one of the most transformative technologies in healthcare. By enabling the fabrication of personalized medical devices, implants, models, and even tissues, 3D printing is not just a technological novelty—it’s a game-changer. Drawing on my years of experience in 3D printing, I’ve witnessed firsthand how these advancements are improving patient outcomes and redefining what’s possible in modern medicine.
Personalized Prosthetics and Orthotics: A Tailored Approach
Traditional prosthetics and orthotic devices often require extensive manual labor and generic sizing that may not fit each patient perfectly. With 3D printing, medical professionals can scan a patient’s limb and design custom-fitted prosthetics that match their unique anatomy. This results in greater comfort, improved function, and a significantly faster turnaround from diagnosis to device delivery.
For children, who outgrow prosthetics quickly, 3D printing offers an affordable and rapid solution for replacement limbs. Clinics and non-profits around the world are leveraging this technology to provide prosthetics to underserved communities, making 3D-printed solutions both accessible and life-changing.
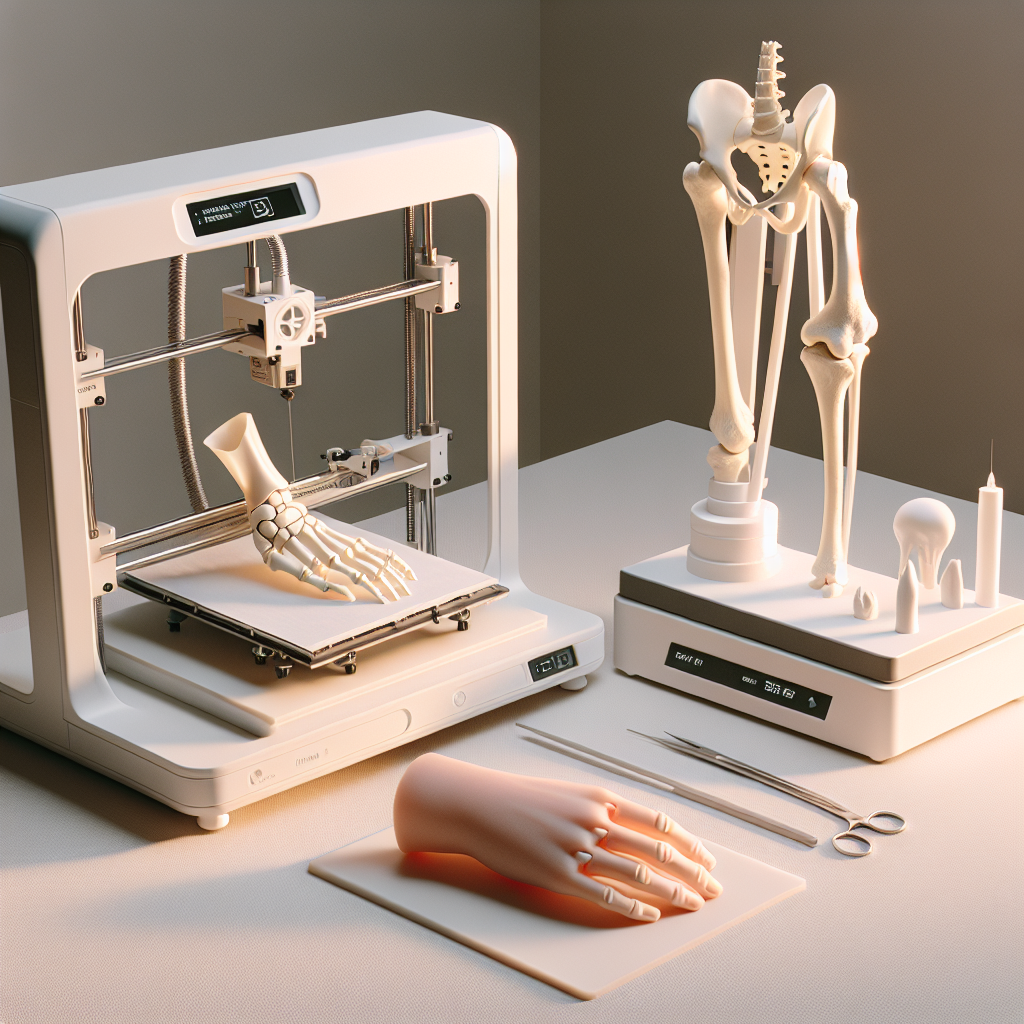
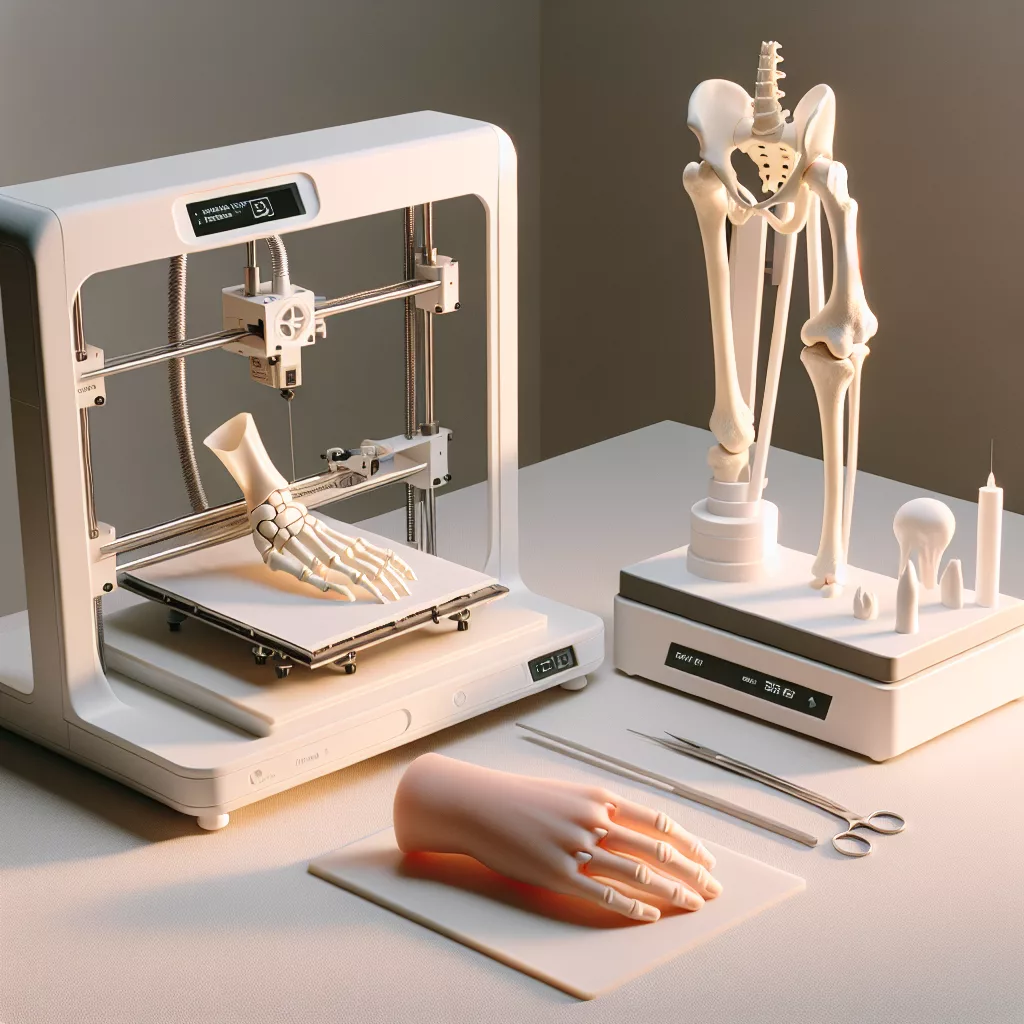
Patient-Specific Surgical Planning with 3D Printed Models
Complex surgeries often require detailed planning to minimize risks and improve outcomes. 3D printing allows surgeons to create exact replicas of patient organs, bones, or tumors based on CT or MRI scans. These models enable surgeons to rehearse procedures, identify potential complications, and choose the most effective surgical approach.
Many hospitals now use these anatomical models for preoperative planning, resulting in shorter surgery times, increased precision, and reduced patient recovery periods. Medical students and residents also benefit from hands-on training using realistic 3D-printed anatomical models.
Custom Implants and Bioprinting: The Future of Regenerative Medicine
One of the most exciting developments in 3D printing is the creation of patient-specific implants. From cranial plates to spinal cages and hip joints, 3D printing enables the design of implants that perfectly match a patient’s anatomy and are made from biocompatible materials like titanium or medical-grade polymers.
Beyond traditional implants, bioprinting—a subset of 3D printing—uses living cells to print tissues and, eventually, organs. While fully functional 3D-printed organs are still in development, early successes include printed skin grafts, cartilage, and vascular structures. The potential is enormous: one day, patients may receive custom-printed organs, eliminating the need for donor waitlists and the risk of rejection.
Rapid Prototyping of Medical Devices
Inventors and medical device companies use 3D printing to prototype new tools and equipment quickly and cost-effectively. This rapid prototyping accelerates the development cycle, allowing for more iterative testing and optimization before mass production. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted this advantage, as 3D printing was used globally to produce vital components like face shields, swabs, and ventilator parts when supply chains were strained.
Dental Applications: Precision and Performance
Dentistry has been one of the earliest adopters of 3D printing technology. Dentists can now scan a patient’s mouth and 3D print crowns, bridges, aligners, and even dentures with unparalleled fit and precision. This not only reduces chair time but also improves patient comfort and outcomes.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its remarkable progress, 3D printing in medicine faces challenges. Regulatory approval processes, reproducibility, and material biocompatibility are ongoing concerns. However, as technology evolves, these hurdles are being addressed with improved printer resolutions, advanced materials, and more robust clinical validation studies.
The future holds immense promise. As 3D printing continues to mature, we can anticipate even more personalized, effective, and accessible healthcare solutions.
Conclusion
3D printing’s impact on medicine is profound and growing. From personalized prosthetics to complex surgical models and tissue engineering, the technology is enhancing patient care, streamlining workflows, and opening doors for innovations previously thought impossible. As someone deeply involved in both 3D printing and healthcare, I’m excited to see how this field will continue to evolve in the years to come, further transforming lives and reshaping the landscape of medicine.


Leave a Reply